<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
<packagingExcludes>
WEB-INF/lib/*.jar,
WEB-INF/classes/META-INF/switchyard.xml
</packagingExcludes>
<webResources>
<resource>
<directory>target/classes/META-INF</directory>
<targetPath>WEB-INF</targetPath>
<includes>
<include>switchyard.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</webResources>
</configuration>
</plugin>
The Administration Guide contains information on how to deploy, configure, and manage the SwitchYard runtime.
Deployment
Packaging
SwitchYard supports the following packaging types for deployment:
-
JAR : the default packaging type for SY apps
-
WAR : useful when you want to include additional libraries with your application and/or you have web application resources (e.g. JSPs, JSF, etc.).
-
EAR : supports multiple application modules in a single deployment along with additional libraries.
For an example of packaging as a WAR, check out the helpdesk quickstart. Pay particular attention to the configuration of the maven-war-plugin to include the SY descriptor and exclude dependencies in the WEB-INF/lib directory which are already available in the SwitchYard runtime.
EAR deployments allow multiple SwitchYard applications to be included in a single deployable archive. Keep in mind that the SY applications included in an EAR are still considered separate applications from a lifecycle and visibility (both class loading and service) standpoint. For an example of deploying a SwitchYard application as an EAR, check out ear-deployment quickstart.
Available Runtimes
SwitchYard 1.0 supports deployment into JBoss Enterprise Application Platform 6.1 . All of the supported deployment mechanisms in EAP are supported, including: file-based, CLI, maven plugin, and console. See the JBoss AS deployment documentation for more information.
Management Console
Overview
The SwitchYard management console is integrated with the standard JBoss AS management console and provides the following:
-
A view of the applications and services deployed on the server.
-
A view of various execution metrics.
-
A view of the SwitchYard subsystem configuration.
SwitchYard contributes views to the standard JBoss AS management console's Runtime and Profile pages.
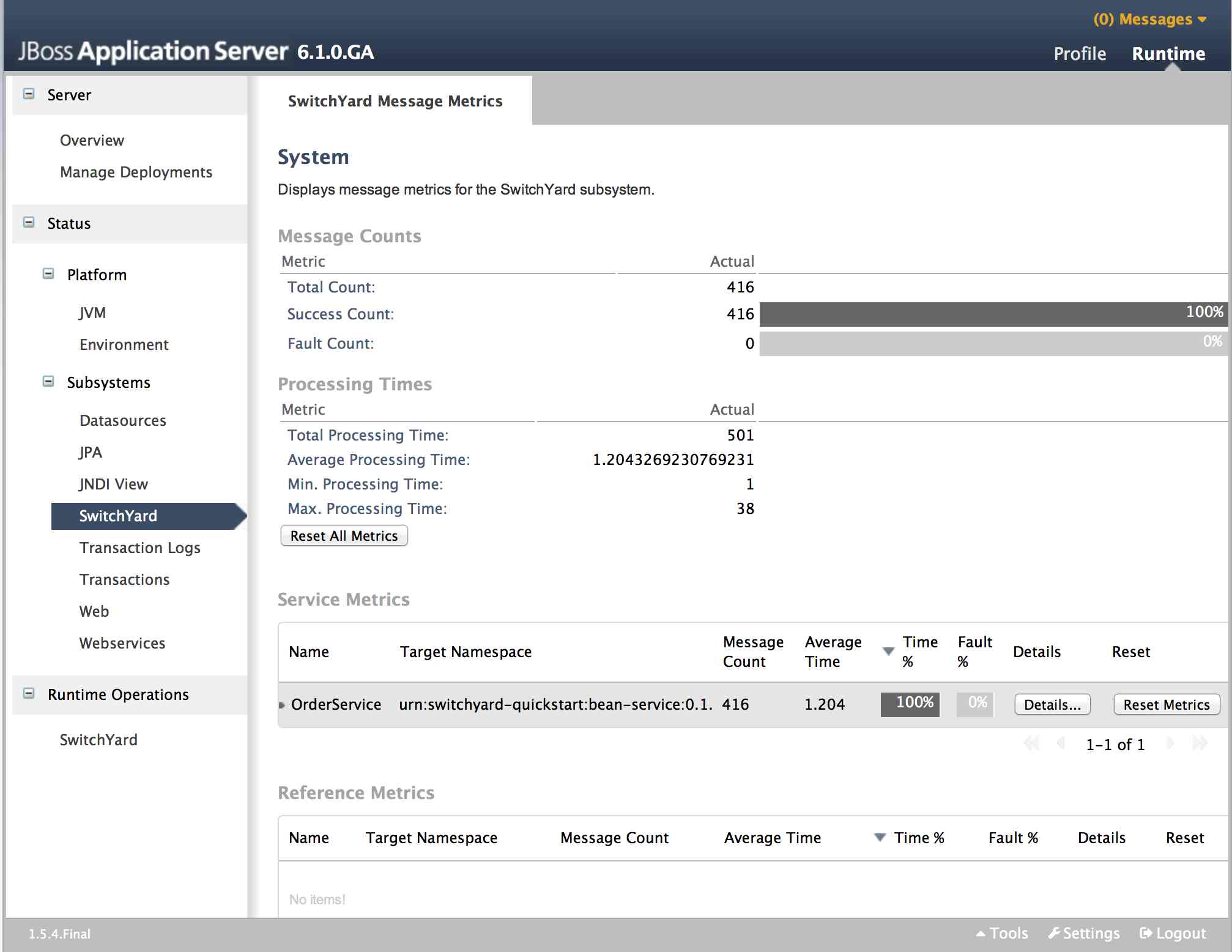
Metrics Views
SwitchYard Message Metrics can be accessed on the Runtime page of the AS console under Status -> Subsystems -> SwitchYard. This page provides a view of a comprehensive set of metrics aggregated at various levels within the system.
The following types of metrics are available:
-
Message count: total, success, failed
-
Processing time: total, min., avg., max.
Collected metrics can be viewed at the following levels:
-
System : metrics for the entire SwitchYard runtime (all deployed applications)
-
Service : metrics for a composite service in an application. Additional metric details are provided for the following:
-
Gateway: metrics for each binding on the service (e.g. FTP metrics for service "ABC")
-
Operation: metrics for each operation on the service
-
Service Reference : metrics for references invoked by the service
-
-
Reference : metrics for a composite reference in an application. Additional metric details are provided for the following
-
Gateway : metrics for each binding on the reference (e.g. FTP metrics for reference "ABC")
-
Operation : metrics for each operation on the reference
-
This page also provides the user with the ability to reset metrics at various levels.
Application Views
SwitchYard contributes a page to the Runtime Operations section which provides views detailing various aspects of SwitchYard applications running on the system. These views may be accessed on the Runtime page of the AS console by selecting Runtime Operations -> SwitchYard. The following views are provided:
-
Applications: lists all SwitchYard applications deployed on the server
-
Services: lists all Services provided by the applications deployed on the server
-
References: lists all service References used by applications deployed on the server
-
Artifacts: lists all artifacts referenced by applications deployed on the server
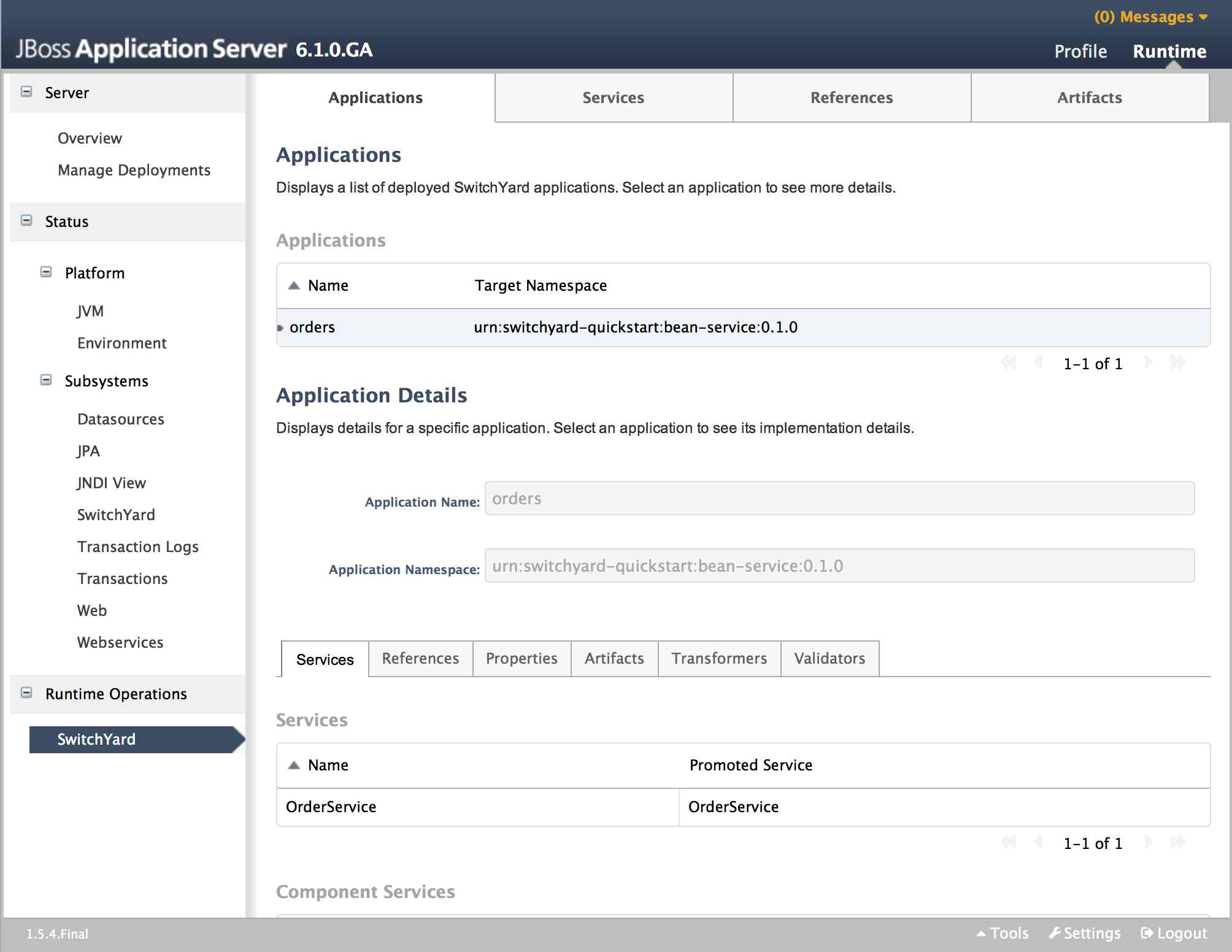
Applications
The main Applications tab displays all the applications deployed on the server. Selecting a particular application in the list will populate the Application Details section below the list. The following details are provided:
-
Services: services provided by the application. Selecting a service will open the main Services tab, displaying details for the service.
-
References: services used by the application. Selecting a reference will open the main References tab, displaying details for the reference.
-
Properties: properties defined in the application. The properties may also be edited within this view.
-
Artifacts: artifacts referenced by the application. Selecting an artifact will open the main Artifacts tab, displaying details for the artifact.
-
Transformers: transformers configured in the application.
-
Validators: validators configured in the application.
Services Tab
The Services tab displays information about the services provided by the application. This information includes the services provided by the application and the component services used to implement the services.
The Services table displays the services provided by the application. The table provides the following details:
-
Name: the name of the service.
-
Promoted Service: the name of the component service providing the implementation for the service.
Clicking on an item in the Name column will load the open the main Services page displaying details for that service. Clicking on an item in the Promoted Service column will highlight the corresponding item in the Component Services table below.
The Component Services table displays the component services defined in the application. This table provides the following details:
-
Name: the name of the component service
-
Interface: the interface implemented by the component
-
Implementation: provides a link for viewing the implementation details of the component
Clicking on an item in the Implementation column will open a dialog detailing the component's implementation.
The Implementation dialog provides the following information:
-
The technology used to implement the component (e.g. Camel).
-
A list of references required by the component.
-
The raw configuration for the implementation.

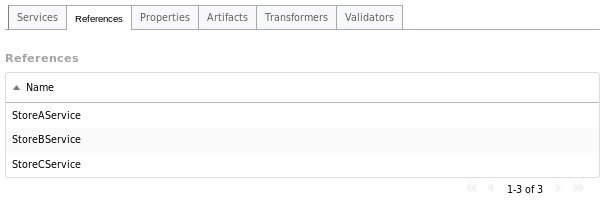
References Tab
The References tab lists all the composite references used by the application.
Properties Tab
The Properties tab provides a list of properties defined in the application. In addition to viewing the properties, this page may be used to update the values for individual properties.
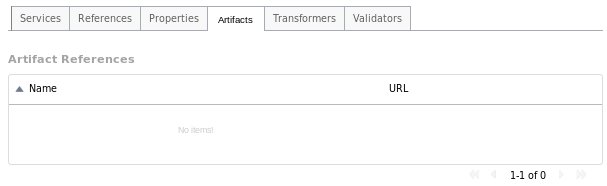
Artifacts Tab
The Artifacts tab provides information about the artifacts referenced by the application and is comprised of a table providing the following details:
-
Name: the name of the referenced artifact
-
URL: the location of the artifact
Clicking on an item in the table will navigate to the main Artifacts page.
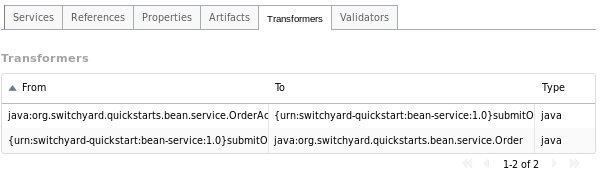
Transformers Tab
The Transformers tab provides details about the transformers deployed by the application, providing the following details:
-
From: the from type supported by the transformer.
-
To: the to type supported by the transformer.
-
Type: the implementation technology used by the transformer (e.g. Java, XSLT, etc.).
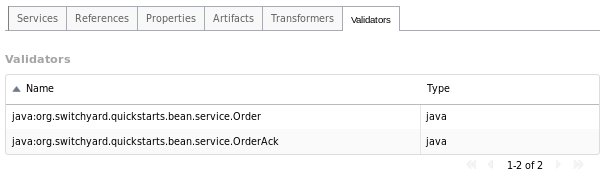
Validators Tab
The Validators tab provides details about the validators deployed by the application, providing the following details:
-
Name: the name of the validator.
-
Type: the type of the validator.
Services
The main Services tab displays all services provided by the deployed applications. Selecting a specific service will populate the Service Details section below the list. Details displayed include:
-
Name: the service name
-
Namespace: the namespace within which the service is defined
-
Application: the application providing the service (this links to the main Applications tab)
-
Interface: the interface provided by the service.
-
Promoted Service: the component service implementing the service.
-
Gateways: lists the gateways providing access to the service.
-
Throttling: throttling configuration for the service
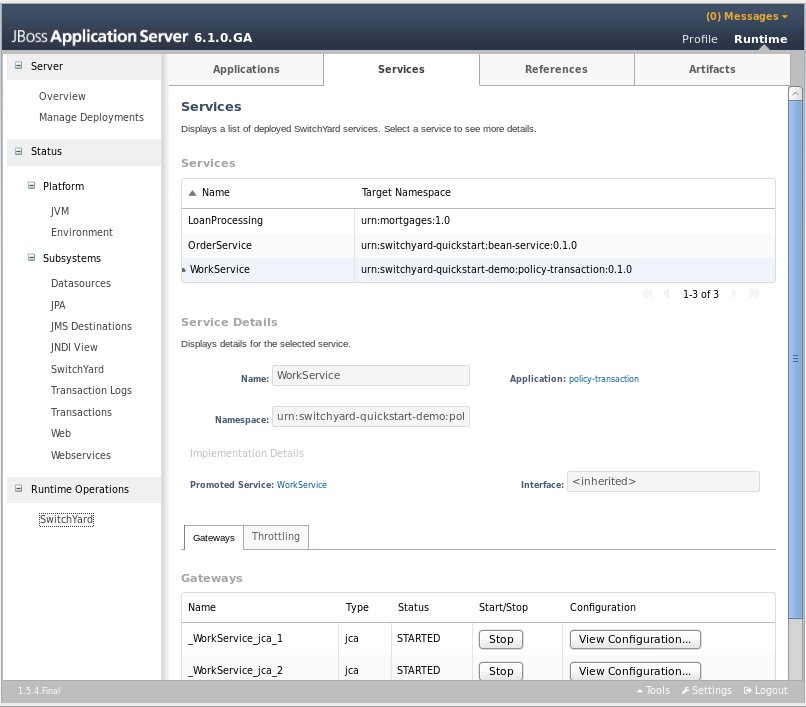
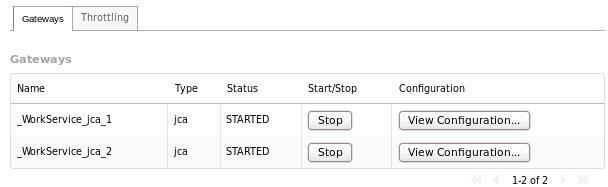
Gateways Tab
The Gateways tab in the details section provides the following information for each of the gateways provided for the service:
-
Name: the name of the gateway
-
Type: the type of the gateway (e.g. SOAP, HornetQ, etc.)
-
Status: the status of the gateway (e.g. started, stopped)
-
Start/Stop: starts or stops the gateway
-
Configuration: opens a dialog displaying the raw configuration for the gateway
Throttling Tab
The Throttling tab in the details section allows the user to view throttling details for the service.
-
Edit: switch to edit mode, allowing the user to change the throttling configuration.
-
Enable: enable/disable throttling for the service
-
Maximum Requests: the maximum number of requests per period before throttling occurs
-
Time Period: the time period over which requests are counted (cannot be edited)

References
The main References tab displays all service references used by the deployed applications. Selecting a specific reference will populate the Reference Details section below the list. Details displayed include:
-
Name: the name of the reference
-
Namespace: the namespace within which the reference is defined
-
Application: the application containing the reference (this links to the main Applications tab)
-
Interface: the interface provided by the reference.
-
Gateways: lists the gateways through which the reference is accessed.
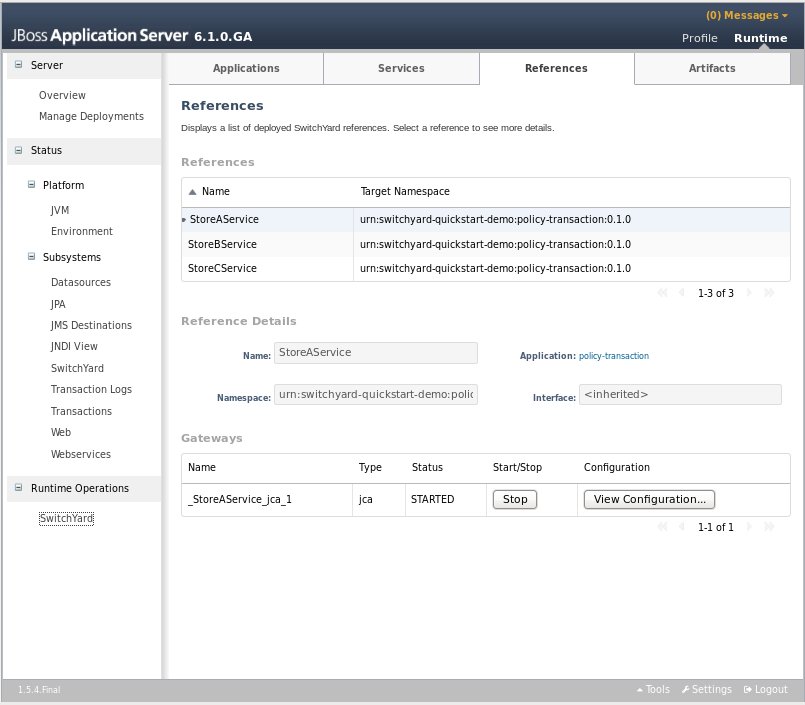
The Gateways section provides the following information for each of the gateways configured for the reference:
-
Name: the name of the gateway
-
Type: the type of the gateway (e.g. SOAP, HornetQ, etc.)
-
Status: the status of the gateway (e.g. started, stopped)
-
Start/Stop: starts or stops the gateway
-
Configuration: opens a dialog displaying the raw configuration for the gateway
Artifacts
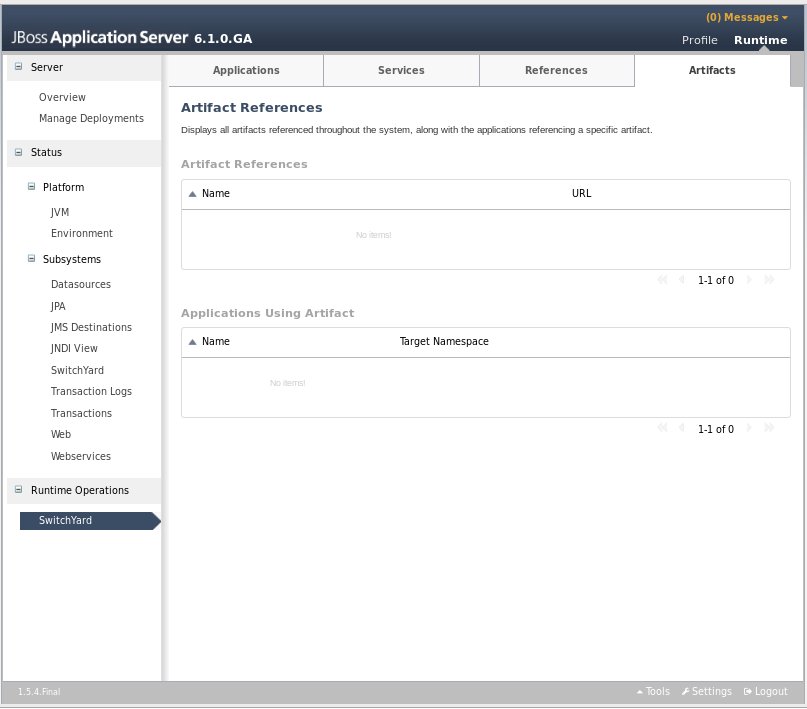
The main Artifacts tab displays all artifacts referenced by applications deployed to the system. Selecting a specific artifact reference will populate the Applications Using Artifact table below. Selecting an application in the applications table will navigate to the main Applications tab.
Subsystem Configuration View
SwitchYard contributes an additional view to the standard JBoss AS management console's Profile page, which can be accessed by selecting the Subsystems -> SwitchYard -> Runtime Details node. This page displays details about to the SwitchYard subsystem configured in the AS configuration profile.
This page displays the version of the SwitchYard runtime, along with a list of installed components. Selecting a component will populate the Component Details section below, which displays:
-
Name: the component name, e.g. SOAP, Camel.
-
Type: the component type, e.g. soap, camel. (The type is the suffix used within switchyard.xml identifying component specific elements, e.g. binding.soap, implementation.camel.)
-
A section providing component specific details. For most components, this section lists any configurable properties and their current settings.

JMX
The core admin API of SwitchYard is wrapped with a set of MBeans allowing for local and remote access for JMX clients. All SwitchYard MBeans are registered under the org.switchyard.admin JMX domain name.
MBeans related to application management are not registered until the first SwitchYard application is deployed.
MBeans
Management.Local
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=Management.Local |
|
Description |
Intended for use by local JMX clients (same VM as the application) to register event listeners with the SwitchYard runtime. |
|
Interface |
Application
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=Application,name="<app-qname>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for a SwitchYard application. |
|
Interface |
Service
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=Service,name="<service-qname>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for a composite service in a SwitchYard application. One MBean is registered per composite service. |
|
Interface |
Reference
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=Reference,name="<reference-qname>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for a composite reference in a SwitchYard application. One MBean is registered per composite reference. |
|
Interface |
Binding
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=Binding,name="<binding-name>",service="<service-qname>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for a gateway binding attached to a composite service or reference. One MBean is registered per binding instance on an application's composite services and references. |
|
Interface |
ComponentService
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=ComponentService,name="<service-qname>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for a component service in a SwitchYard application. One MBean is registered per component service. |
|
Interface |
ComponentReference
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=ComponentReference,name="<reference-qname>,service="<service-qname>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for a component reference in a SwitchYard application. One MBean is registered per component reference. |
|
Interface |
Transformer
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=Transformer,name="<from-type> => <to-type>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for a transformer in a SwitchYard application. One MBean is registered per transformer. |
|
Interface |
Validator
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=Validator,name="<type>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for a validator in a SwitchYard application. One MBean is registered per validator. |
|
Interface |
Throttling
|
ObjectName |
org.switchyard.admin:type=Throttling,service="<service-qname>" |
|
Description |
Management interface for throttling a service in a SwitchYard application. One ThrottlingMBean is registered per composite service instance. |
|
Interface |
Lifecycle
|
ObjectName |
none |
|
Description |
Supertype of BindingMXBean which provides operations related to lifecycle control for service and reference bindings. |
|
Interface |
Metrics
|
ObjectName |
none |
|
Description |
Supertype of multiple MBeans providing message metrics information. |
|
Interface |
BPEL Console
The BPEL console can be deployed to SwitchYard through its installer since SwitchYard-0.4 version.
Overview
This section provides an overview of the BPEL Console. The console provides the ability to view:
-
The process definitions deployed to the BPEL engine
-
The process instances executing in the BPEL engine
-
The execution history of a process
-
The history instances query
Installation
The easiest way to install the BPEL console is to download the SwitchYard installer and then run :
ant install-bpel-console
You will then be prompted for the location of your EAP installation, and the Installer will place the necessary WAR files in EAP.HOME/standalone/deployments.
Alternatively, you can just simply copy the switchyard-bpel-console.war folder and switchyard-bpel-console-server.war from the Tools distribution into the EAP_HOME/standalone/deployments folder. Remember that you will need to add a marker file named "switchyard-bpel-console.war.dodeploy" in the deployments folder as well to trigger the deployment.
Because of this issue (https://issues.jboss.org/browse/RIFTSAW-391), we used the exploded war of the switchyard-bpel-console as the workaround.
Logging in
The BPEL console can be located using the URL: http://localhost:8080/bpel-console.
It is recommended that you only open one bpel-console window within your browser, otherwise, you may see blank window once you logged in, or couldn't log in from your second window. For detail please see RIFTSAW-400.
The first screen that is presented is the login screen:
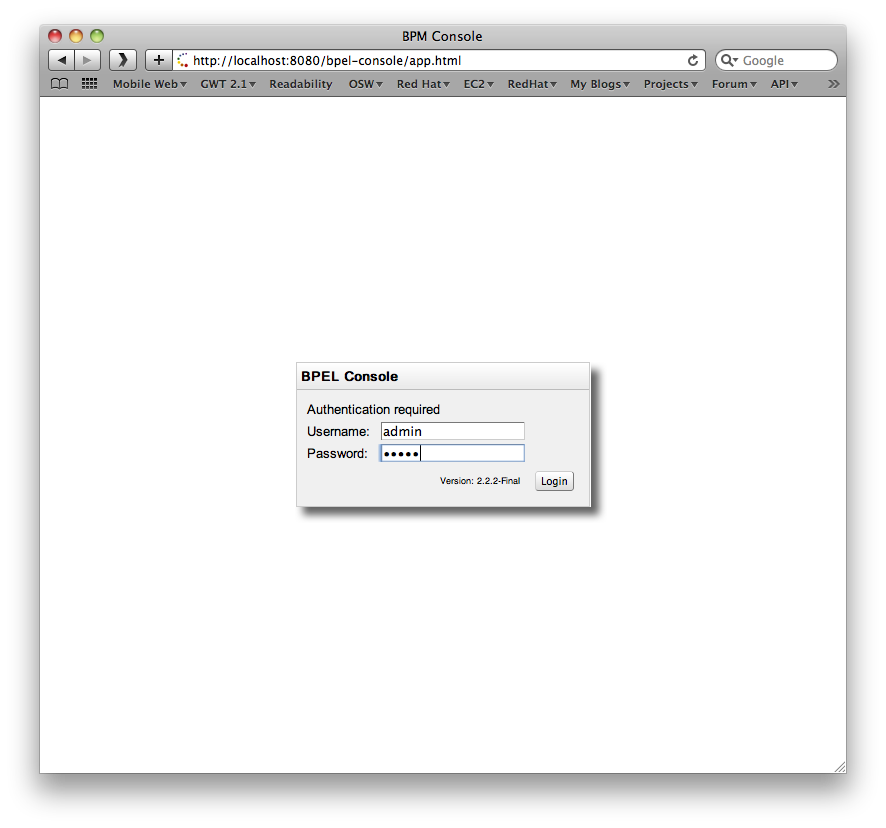
The default username is admin with password admin.
The Access Control mechanism used by the admin console is configured in the $deployFolder/bpel-console/bpel-identity.sar/META-INF/jboss-service.xml. The JAAS login module is initially set to use a property file based access mechanism, but can be replaced to use any appropriate alternative implementation.
The users for the default mechanism are configured in the property file $deployFolder/bpel-console/bpel-identity.sar/bpel-users.properties. The entries in this file represent username=password.
The user roles for the default mechanism are configured in the property file $deployFolder/bpel-console/bpel-identity.sar/bpel-roles.properties. The entries in this file represent username=role. The only role of interest currently is administrator.
Deployed Process Definitions
Once logged in, the 'Manage Instances' tab shows the currently deployed BPEL processes and their versions.
Process Instances
When a process definition is selected (Open), the list of active process instances for that process definition (and version) will be displayed in the bottom panel.
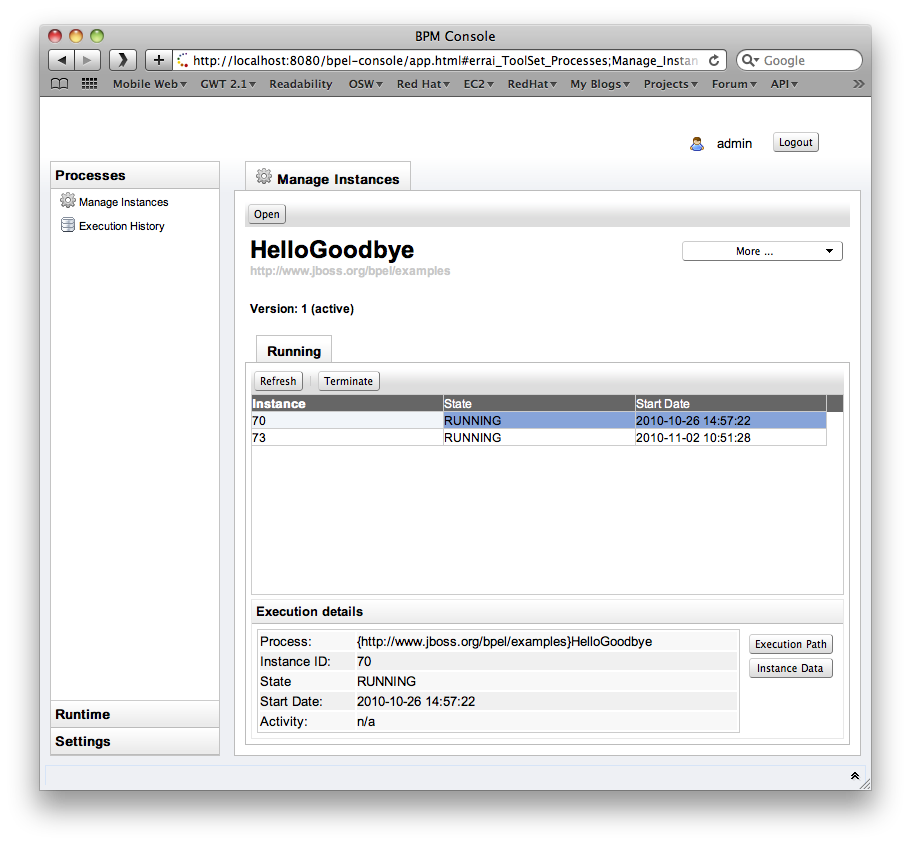
Process Versions
There is only one active version at a time. If you open a process definition the active version will be chosen by default. Sometimes you need to manage instances of a retired version (i.e. to terminate running instances). In that case the button More - Change Version allows you to select a different version of that process.

Execution History
The Execution History allows you to inspect the BPAF history data associated with a process. You can specify a timespan and whether or not you'd like to see failed/terminated instances included in the chart.
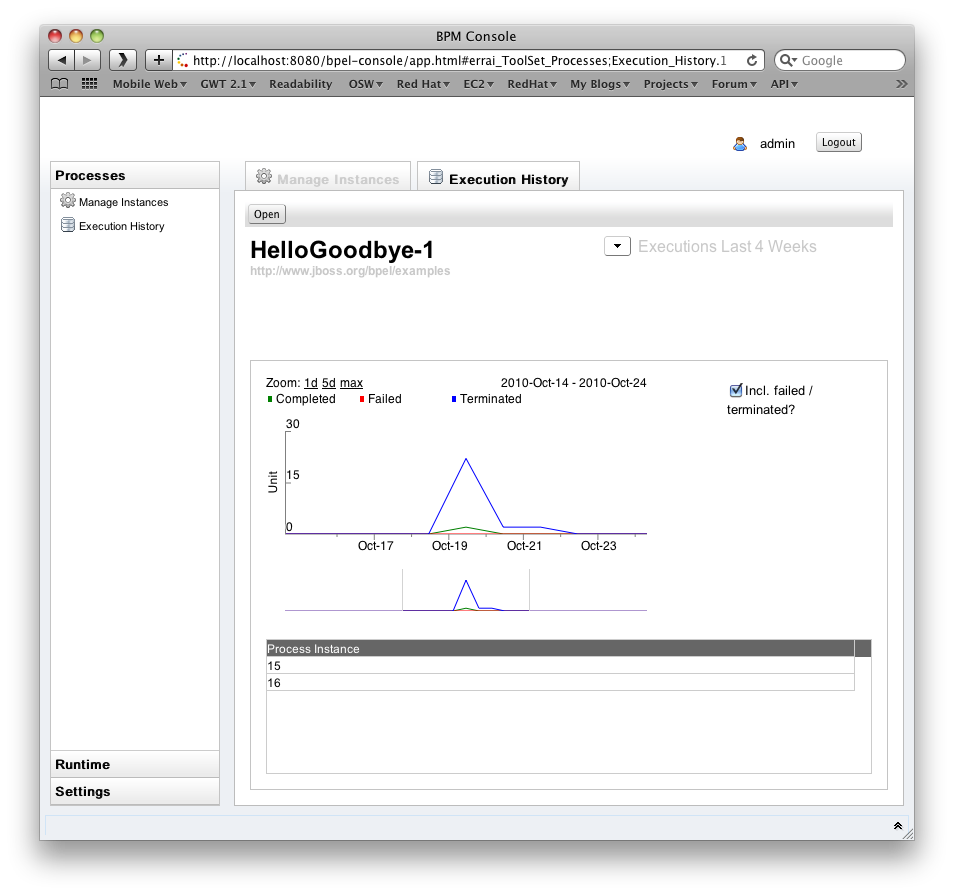
The chart has various keyboard bindings to browse through the displayed execution data:
|
Key |
Action |
|
Up Arrow |
Zoom In |
|
Down Arrow |
Zoom Out |
|
Left Arrow |
Half-Page Left |
|
Right Arrow |
Half-Page Right |
|
Page-Up |
Page Left |
|
Page-Down |
Page Right |
|
TAB |
Next Focus |
|
Shift-TAB |
Previous Focus |
|
HOME |
Max Zoom Out |
|
ENTER |
Max Zoom In to Focus |
|
Mouse Drag |
Scroll Chart |
|
Shift Mouse Drag |
Drag Select/Zoom |
|
Mouse Wheel Up/Z |
Zoom In |
|
Mouse Wheel Down/X |
Zoom Out |
|
Backspace/Back Button |
Back |
|
Right Mouse Button |
Context Menu |
|
Left Click |
Set Focus |
|
Double Click |
Max Zoom In to Focus |
Logging configuration options
You need to explicitly enable history logging for a particular process through the 'deploy.xml' file and for the BPEL engine in general through the 'bpel.properties' file. In order to record history data, set the 'process-events' option for a particular process and make sure the 'org.jboss.soa.bpel.console.bpaf.BPAFLogAdapter' is enabled.
Process configuration example (deploy.xml):
<deploy xmlns="http://www.apache.org/ode/schemas/dd/2007/03"
xmlns:bpl="http://www.jboss.org/bpel/examples"
xmlns:intf="http://www.jboss.org/bpel/examples/wsdl">
<process name="bpl:HelloGoodbye">
<active>true</active>
<process-events generate="all"/>
<provide partnerLink="helloGoodbyePartnerLink">
<service name="intf:HelloGoodbyeService" port="HelloGoodbyePort"/>
</provide>
</process>
</deploy>
Instance Data and Execution Path
When a process instance is selected, its details will be displayed in the Execution Details panel. The Instance Data button will also become enabled, allowing further detail about the process to be displayed. Likewise the Execution Path button opens the related instance execution graph.

The View tab shows the instance execution graph, while the Source tab below shows all activity events
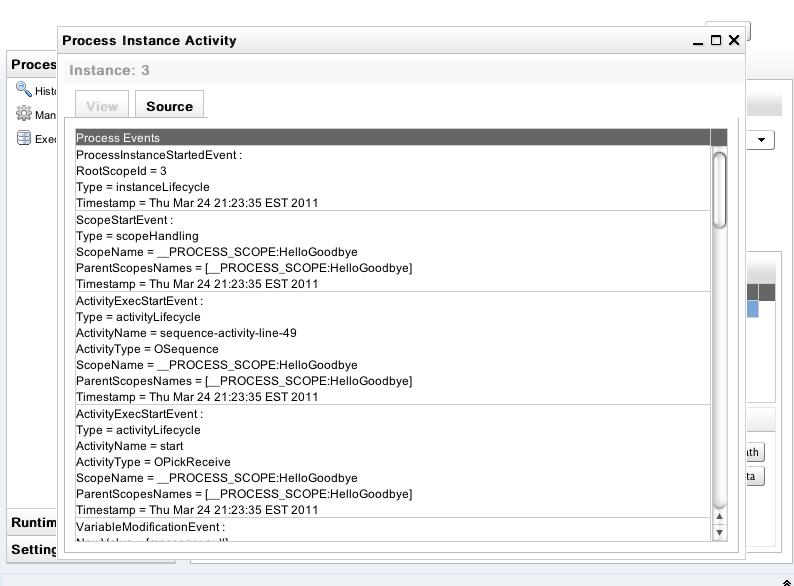
History Instance Query
Once a process instance is finished, could be 'COMPLETED', 'FAILD' or 'TERMINATED', you could search it through the History Query tab window as following:
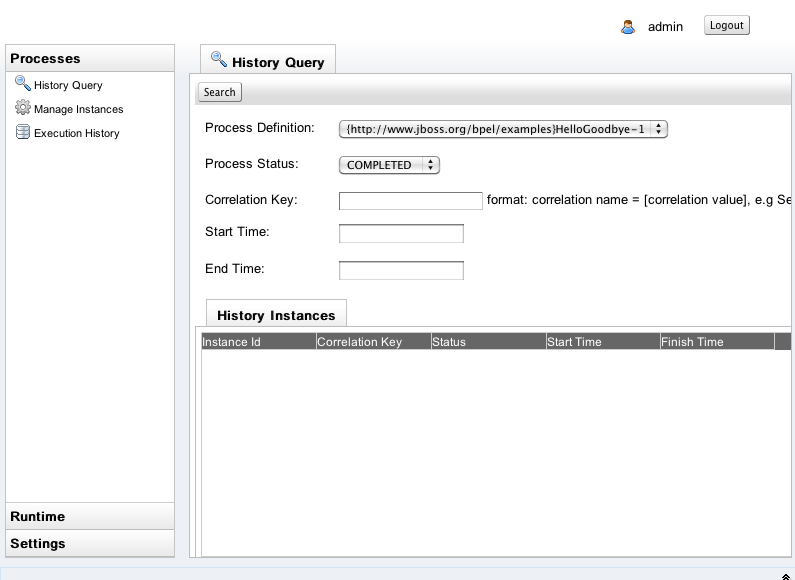
You need to choose the Process Definition and the Process Status from the list box. You could also input the correlation key, start time and end time as criteria to search the history instances. Below is the search result.
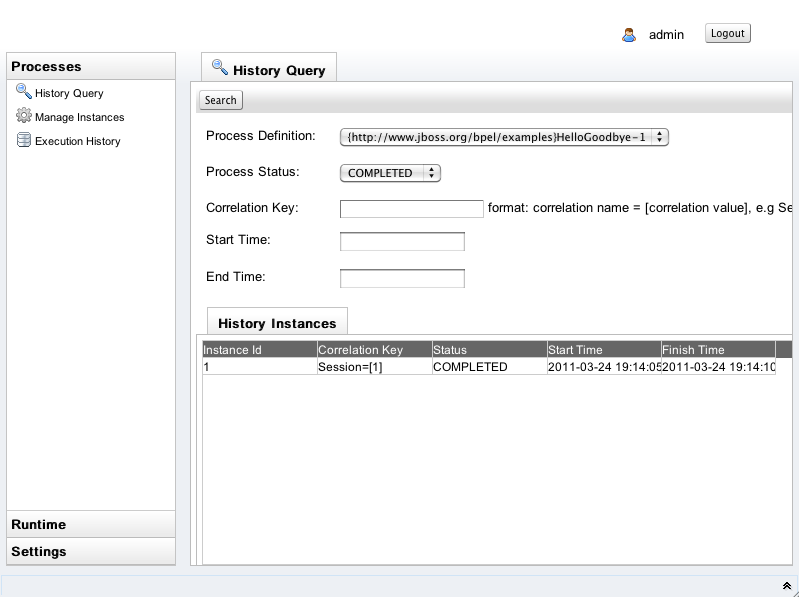
On the History Instances List, when you double click a specific row, it will pop up a window that shows all of execution events that happened during this process instance execution.
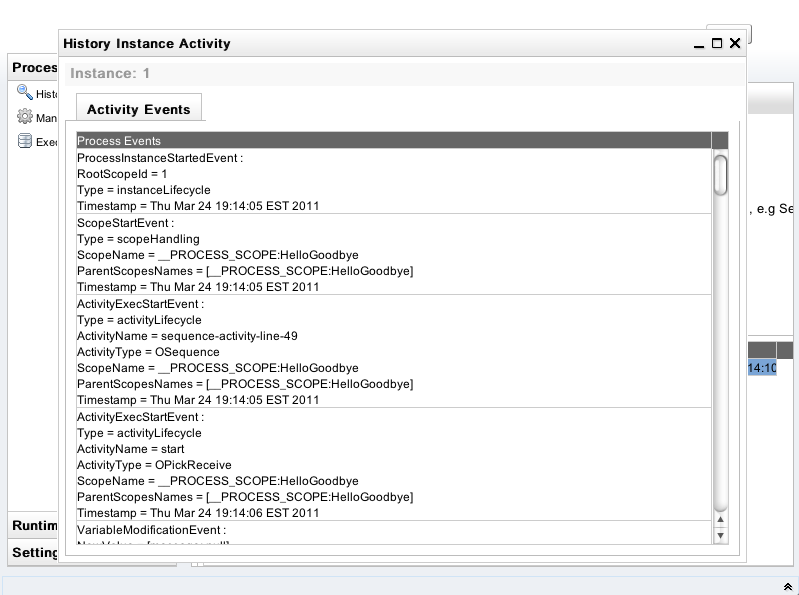
Please be noted that you have to explicitly enable the history logging in order to use the History Query functionality.
Retiring and Reactivating Process Definitions
When a process definition is initially deployed (i.e. the first version of the process), it automatically becomes the active process definition. If that BPEL process definition is subsequently change and redeployed, then the previous version is retired, and the new version becomes the active version.
The only difference between an active and retired process definition is that a retired process definition can no longer create new process instances. However if there are current process instances associated with the retired process definition version, then these will continue to execute.
On some occasions, the administrator may wish to change which version of a process definition is considered the <emphasis>active</emphasis> version. Or they may simply want to retire the currently active process definition, so that no more process instances can be created, only allowing the already running process instances to continue until completed.
To change the status of a process definition, the administrator should select the Runtime tab from the lefthand panel, and then select the Deployments option. This will show the process definitions, their versions and their current status (active or retired).
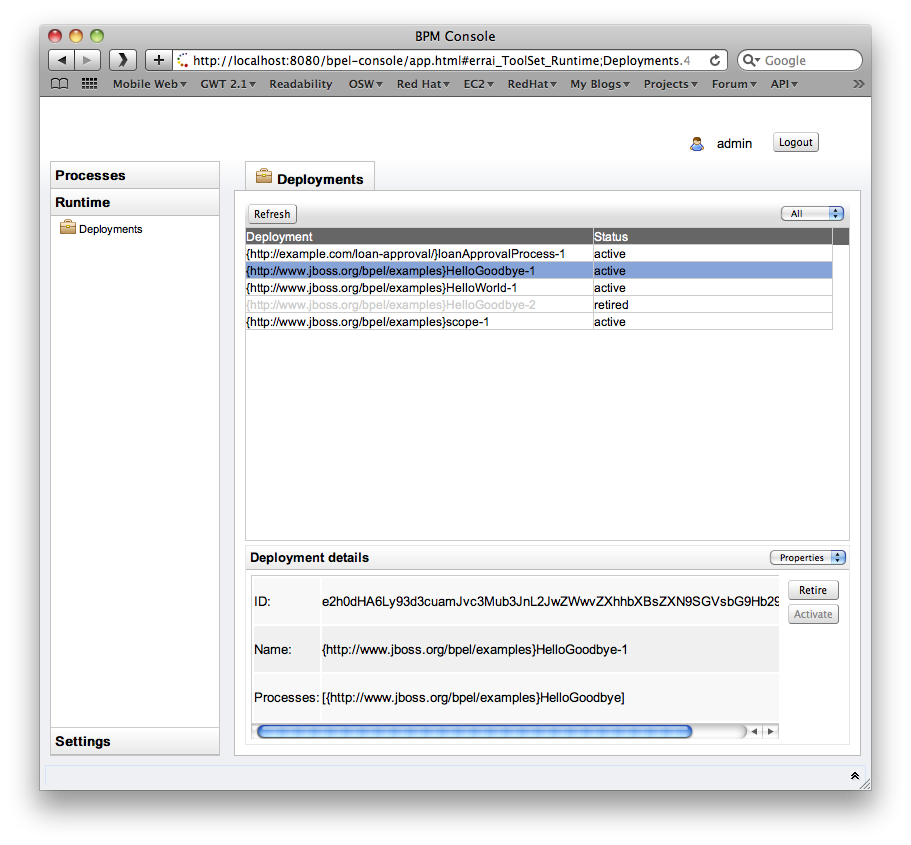
BPEL Database Configuration
Overview
In BPEL component, we are using the in-memory H2 database, this page is trying to give you an example that update it to a Mysql database.
Changing database steps
Download db ANT script.
Download the db ANT script zip from here, we use the RiftSaw-3.0.0 Final release (used in SwitchYard 1.0.0.Final) as an example.
Create and install the mysql database driver.
-
create the folder in $SwitchYard/modules/mysql/main, and then copy the mysql-connector-java-5.1.12.jar (of course, you can choose other versions, but in this page, we are using this version as an example) inside it.
-
create a module.xml along with it, the content is like following:
<module xmlns="urn:jboss:module:1.1" name="mysql"> <resources> <resource-root path="mysql-connector-java-5.1.12.jar"/> </resources> <dependencies> <module name="javax.api"/> <module name="javax.transaction.api"/> </dependencies> </module> -
add the mysql driver and the datasource in standalone.xml file.
<subsystem xmlns="urn:jboss:domain:datasources:1.0"> <datasources> ..... <datasource jndi-name="java:jboss/datasources/BpelDS" enabled="true" use-java-context="true" pool-name="BpelDS"> <connection-url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/riftsaw</connection-url> <driver>mysql</driver> <pool/> <security> <user-name>root</user-name> <password>jeff</password> </security> </datasource> <drivers> ... <driver name="mysql" module="mysql"> <driver-class>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driver-class> </driver> </drivers> </datasources> </subsystem>
Update the database information, and run ANT script to populate the riftsaw schema
Go to the folder that you have extracted for db script zip that we downloaded earlier, let us call it '$dbscript'.
-
update the jdbc properties properly in $dbscript/jdbc/mysql.properties. (for other databases, update other $database.properties file)
-
update the build.xml file's database property as your target db, (mysql in this case)
-
run following command to populate the schema:
ant create.riftsaw.schema
you should be able to view the tables via: ant db.show.tables command, and drop the database script through: ant drop.riftsaw.schema
Override the properties for bpel component in standalone.xml file
Go to the $SwitchYard/standalone/configuration/standalone.xml, find the BPELComponent, and then overriding following properties:
<module identifier="org.switchyard.component.bpel" implClass="org.switchyard.component.bpel.deploy.BPELComponent">
<properties>
<bpel.db.mode>EXTERNAL</bpel.db.mode>
<db.emb.create>false</db.emb.create>
<bpel.db.ext.dataSource>java:jboss/datasources/BpelDS</bpel.db.ext.dataSource>
<hibernate.dialect>org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect</hibernate.dialect>
</properties>
</module>
Then you should be ready to start the SwitchYard, the BPEL component will use the database that you created.